Future of Industrial Communication: AI-Assisted Troubleshooting and Predictive Alerts

Introduction
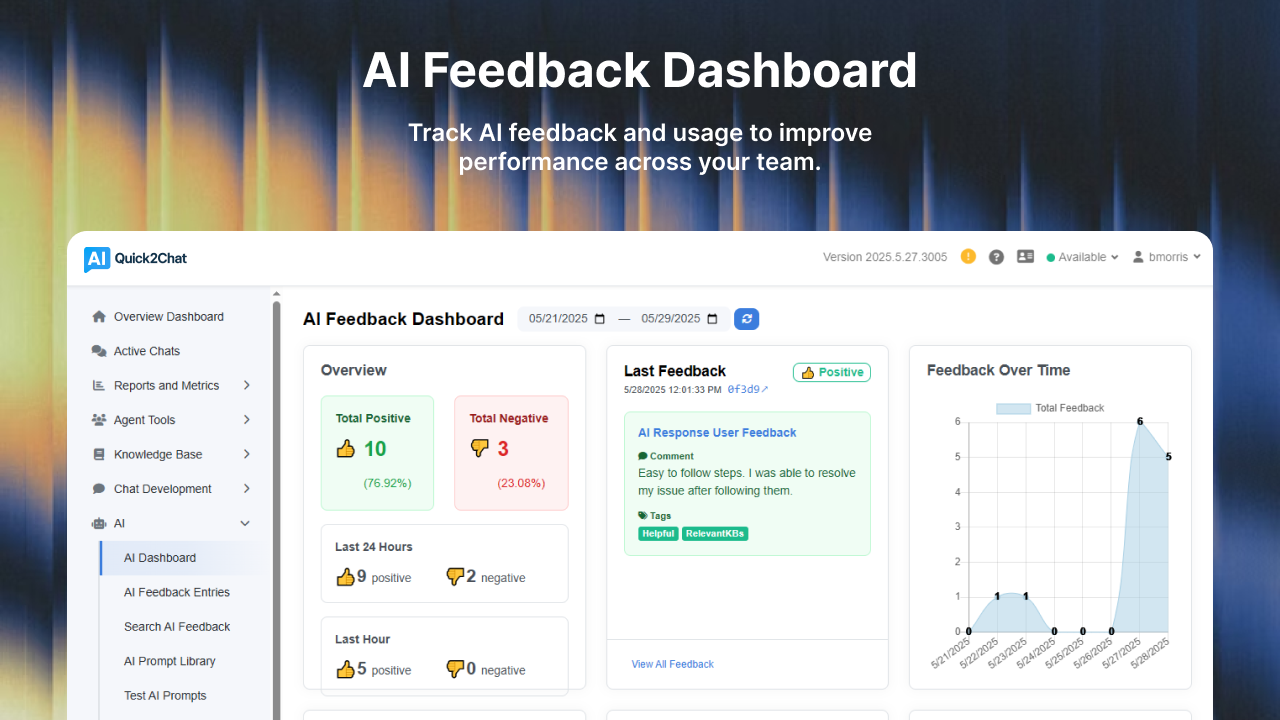
Industrial communication is undergoing a transformative shift as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies reshape how manufacturing facilities detect, diagnose, and resolve operational challenges. The convergence of Industry 4.0 technologies with advanced AI capabilities is creating intelligent communication systems that not only facilitate human interaction but actively participate in troubleshooting and maintenance processes. Research indicates that AI-driven predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by up to 40% and decrease downtime by up to 50%, while unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers an estimated $50 billion annually (1, 2).
This article explores the emerging capabilities that are defining the future of industrial communication, with particular focus on automated diagnostic suggestions, pattern recognition in equipment discussions, and intelligent escalation systems.
AI-Assisted Troubleshooting: The Rise of Conversational Intelligence
Natural Language Processing in Industrial Environments
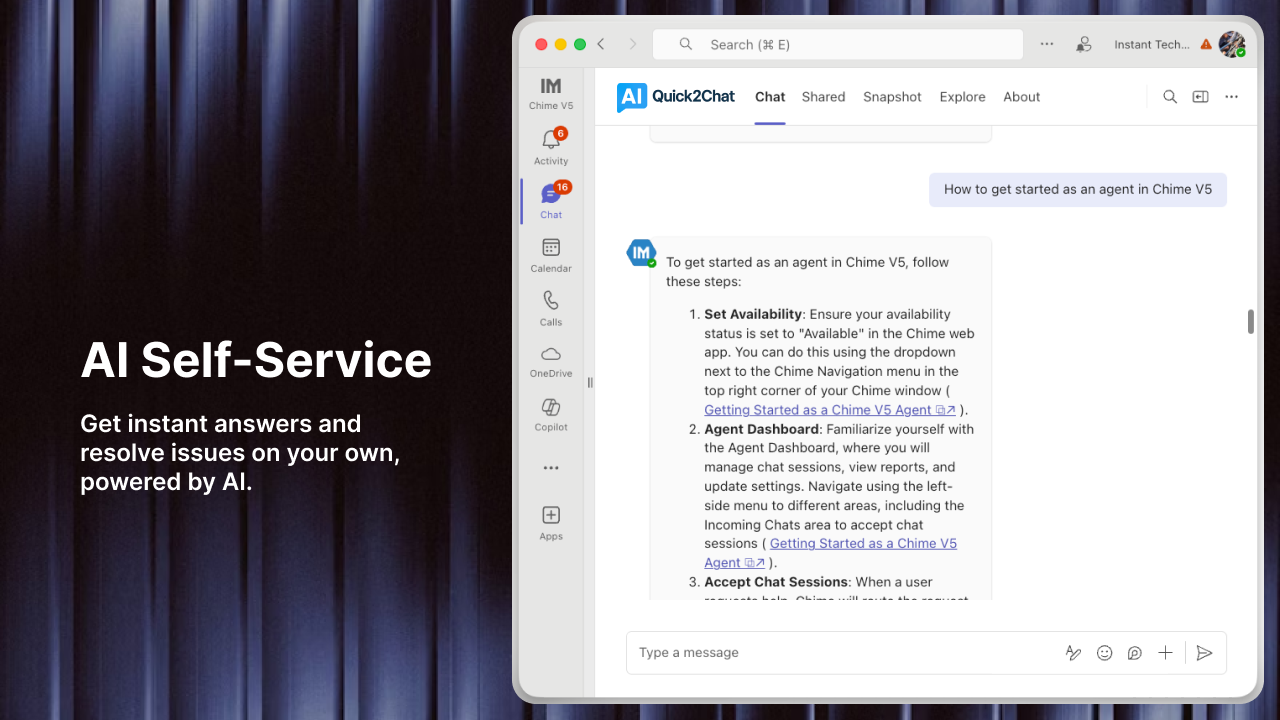
The integration of Natural Language Processing (NLP) into industrial chat services represents a fundamental shift in how operators interact with manufacturing systems. Unlike traditional rule-based chatbots that rely on predefined scripts and keywords, modern NLP-powered systems employ machine learning algorithms to understand the subtleties of human communication, including intent, context, and sentiment (3).
Recent experimental research demonstrates the practical application of these systems. A study published in The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology examined a hybrid AI and generative AI chatbot designed for Industry 5.0 contexts (4). The system integrated a Langchain agent linked to the OpenAI GPT-3.5 language model, feeding it with factory-monitored data to extract equipment conditions useful for troubleshooting and predictive maintenance analysis. The experimental results showed significant accuracy when retrieving data based on specific prompts and demonstrated advantages in reduced troubleshooting time compared to operations in traditional factories that depend heavily on supervisor interventions. The system processing time for troubleshooting prompts averaged less than 10 seconds, effectively eliminating the waiting period for maintenance supervisor analysis (4).
Context-Aware Diagnostic Systems
Modern AI-assisted troubleshooting systems go beyond simple keyword matching. These systems leverage machine manuals, real-time machine data, and historical maintenance records to provide comprehensive diagnostic support (5). By seamlessly integrating this information into their decision-making processes, AI systems can analyze and understand problem complexity more comprehensively than conventional case management tools. This transformation extends across multiple industries including manufacturing, field operations, telecommunications, utilities, and financial services (5).
Research indicates significant benefits from implementing NLP chatbots in industrial applications (6, 7):
| Metric | Improvement | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Labor costs | 52% reduction | Significant cost savings |
| Routine inquiries handled | 80% automated | Reduced workload on staff |
| Manager efficiency | 33% increase | Better resource utilization |
| User satisfaction | Up to 91% | High acceptance rates |
In industrial applications, NLP chatbots can quickly guide workers through troubleshooting steps and escalate to supervisors when necessary, ensuring seamless resolution of technical and logistical issues (7).
Pattern Recognition in Equipment Discussions
Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection
One of the most significant advances in industrial communication involves AI's capability to recognize patterns in equipment behavior and discussions. Using machine learning techniques, systems can now identify anomalies that would be impossible for humans to detect manually, particularly in industrial settings with thousands of sensors generating vast quantities of data (8).
A comprehensive review of anomaly detection methods found that machine learning algorithms can detect anomalies in industrial equipment with high accuracy (9). In one study focused on applications driven by electric motors, the k-NN model (K=3) achieved exceptional results in a test set of 627 samples, with only nine errors in anomaly detection across overload and unbalanced conditions (9). This level of precision enables early intervention before equipment failures occur.
Research published in the journal Electronics demonstrated that various machine learning algorithms show distinct performance characteristics depending on the dataset and industrial context (10):
| Algorithm | Performance Characteristics | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) | High accuracy (only 9 errors in 627 samples) | Electric motor anomaly detection |
| Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) | High accuracy in anomaly detection | General industrial equipment |
| Support Vector Machines (SVM) | Outperforms other models on certain datasets | Specific industrial contexts (requires more runtime) |
| Random Forests | Higher accuracy and faster processing | Alternative datasets requiring speed |
| Deep Neural Networks (DNN) | Varies by dataset | Complex pattern recognition |
This diversity highlights the importance of selecting appropriate algorithms based on specific industrial requirements (10).
Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis
Modern industrial environments leverage Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sophisticated pattern recognition in both visual and time-series data (11). CNNs have demonstrated exceptional performance in detecting visual anomalies through automatic and hierarchical learning of spatial hierarchies, making them particularly effective for industrial quality control scenarios. Meanwhile, Simple Recurrent Units (SRUs) effectively capture temporal dependencies in time-series data, offering advantages for real-time anomaly detection in dynamic systems such as predictive maintenance in machinery (11).
A study on smart industrial machinery plants described an architecture using Apache Kafka and Apache Flink technologies to facilitate real-time data transmission and processing (12). The system employs machine learning models, including CNNs and Hidden Markov Models (HMM), designed to identify patterns and abnormal behaviors in data from sensors and cameras. This continuous monitoring approach enables anomaly detection as data is generated, allowing immediate response to equipment issues (12).
Deep Learning for Complex Pattern Recognition
Advanced deep learning frameworks have shown remarkable success in detecting subtle patterns in industrial equipment. Research on gearbox fault diagnosis using a 6-layer autoencoder-based deep learning model achieved 91% overall accuracy in anomaly detection (13). By analyzing vibration signals, these systems can determine the nature and severity of defects in machinery, enabling early fault detection before catastrophic failures occur. The study demonstrated that examining vibration signals using deep learning techniques allows the system to identify fault signatures in equipment components (13).
Predictive Alerts: From Reactive to Proactive Communication
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance Systems
The evolution from reactive to predictive maintenance represents a paradigm shift in industrial communication. AI-driven predictive maintenance monitors equipment performance and predicts breakdowns using advanced machine learning algorithms, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics (14). This proactive strategy decreases unplanned downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the longevity of essential machinery.
Leading industrial organizations have demonstrated the value of these approaches (14):
| Organization | Application | Technology Used | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siemens | Manufacturing equipment monitoring | AI and IoT | Transformed downtime and maintenance expenses |
| GE Aviation | Jet engine fault prediction | Aircraft sensor data analysis | Proactive maintenance scheduling for safety and reliability |
The recent convergence of edge AI and 5G connectivity, anticipated for 2025-2026, enables unprecedented real-time responsiveness in predictive maintenance (15). Edge AI processing at the device or local node eliminates the roundtrip latency inherent in cloud-based systems. When paired with 5G's ultra-low-latency connectivity, tasks such as rerouting work, throttling operations, or shutting down equipment to prevent damage become feasible in real time. Industry data suggests that unplanned network or equipment downtime in manufacturing can cost up to $1 million per hour in high-precision industries like semiconductor manufacturing (15).
Digital Twin Integration
Digital twin technology plays a vital role in fulfilling the requirements of Industry 4.0 by providing digital representations of factory operations, communication networks, and logistics systems (16). Through the integration of AI technologies, digital twins enable real-time simulations and scenario studies that give manufacturers unprecedented insights into equipment performance and failure processes (17).
The sophistication of digital twins depends on the processes represented and available data. By placing sensors on particular assets, gathering data, creating digital duplicates, and employing machine intelligence, manufacturers can understand how assets will behave in real-time in the physical world (16). This capability supports the transition from reactive to predictive maintenance, and eventually to prescriptive maintenance, where AI predicts faults and suggests specific fixes (17).
Research on digital twin applications in Industry 4.0 emphasizes their ability to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, improve decision-making processes, and streamline industrial operations (18). The technology leverages advancements in IoT, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and big data to create dynamic, real-time replicas of physical systems (19). As Industry 5.0 emerges with greater emphasis on human-centered sustainability and flexibility, digital twins combined with AI are becoming essential for intelligent management, control, and system integration (20).
Intelligent Escalation: Smart Routing of Critical Issues
AI-Powered Escalation Management
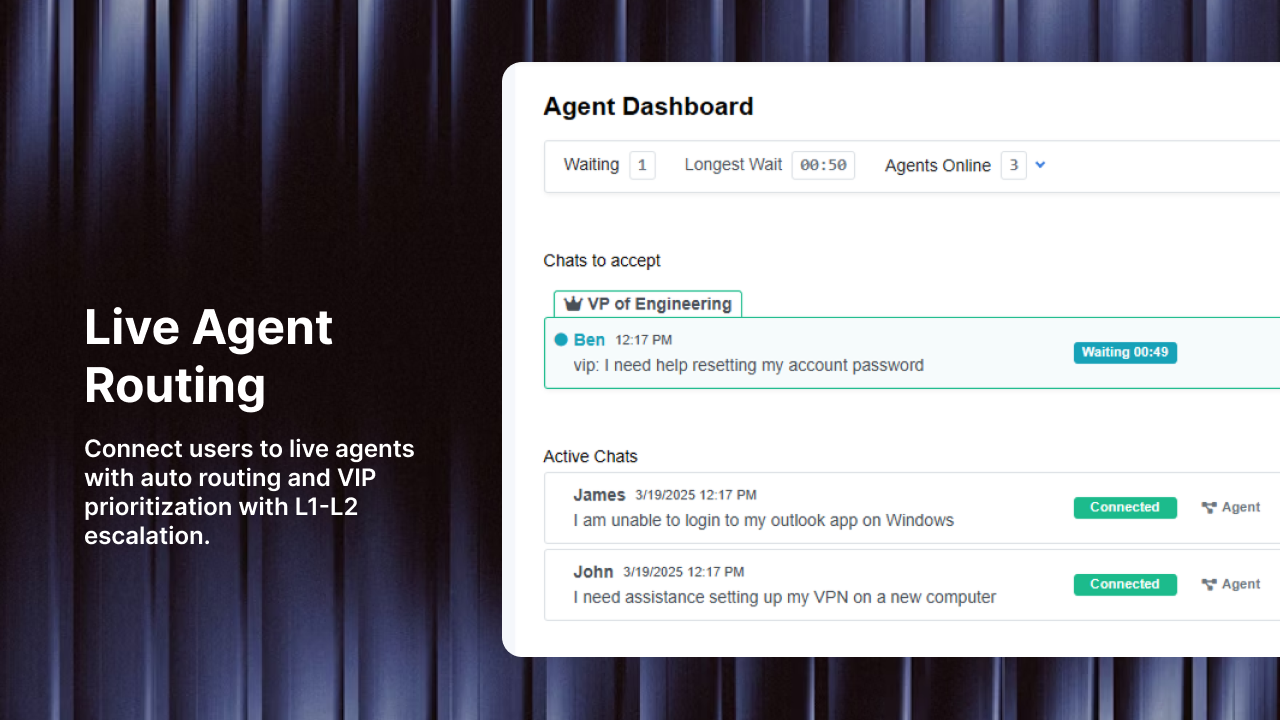
Intelligent escalation systems represent a critical evolution in industrial communication, automatically detecting, prioritizing, and routing critical business issues to appropriate decision-makers based on predefined rules and real-time data analysis (21). When production line sensors detect equipment anomalies, these systems immediately alert maintenance teams with the appropriate expertise level, preventing costly downtime. Organizations implementing automated escalation management report reductions in average response times of up to 65% compared to traditional escalation methods (21).
Research on escalation management in manufacturing identifies several key challenges that AI addresses (22):
| Challenge | Traditional Approach | AI Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Delayed communication across shifts | Manual handoffs, missed information | Real-time detection and routing |
| Information gaps | Missing context in escalations | Context-rich alerts with historical data |
| Overload of incidents | Everything appears urgent | Intelligent prioritization based on severity |
| Lack of feedback loops | Discourages future reporting | Automated tracking and resolution confirmation |
AI-powered problem-solving tools change this dynamic by detecting problems in real time, routing them to the right people, and ensuring fast, accountable resolution (22).
Context-Rich Alert Systems
Modern intelligent alerting systems use AI and ML to generate smart alerts by adding valuable technical and business context (23). These alerts become intelligent when enriched with information including affected services, related systems, historical patterns, business impact, topology data, and change records. By harnessing AIOps and intelligent alerting, teams can cut through noise to focus on incidents that truly matter, enhancing both efficiency and system reliability (23).
Advanced escalation platforms deliver risk-based recommendations and alerts with governance controls ensuring data accuracy and traceability for proactive decision-making (24). These governed, traceable predictions and escalation workflows reduce operational risk, support safety and regulatory compliance, and give leaders confidence in AI-driven decisions. The systems detect early-warning signals weeks before failures occur and optimize maintenance schedules with prioritized risk assessments (24).
Real-Time Intelligent Routing
AI-driven escalation workflows can detect high-priority incidents, categorize them based on severity, and route them to the right teams in real-time, ensuring faster response and resolution (25). Systems like these consolidate alerts from various monitoring sources, filter out noise, and ensure incidents are routed to appropriate teams with actionable insights and historical context. They deliver instant notifications via multiple communication channels (25):
| Channel | Use Case | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed incident reports | Comprehensive information delivery | |
| SMS | Critical alerts | Immediate mobile notification |
| Microsoft Teams | Team collaboration | Integrated workflow communication |
| Slack | Cross-team coordination | Real-time team updates |
| ITSM Dashboards | Centralized monitoring | Complete incident visibility |
In manufacturing contexts, intelligent escalation is not merely automation but risk-based decision-making embedded into daily workflows (22). For example, when Statistical Process Control (SPC) systems monitor trends and detect early deviations, the system alerts line leads and process engineers before control limits are breached, with attached control charts and defect risk projections. This early intervention saves batches and enables immediate corrective action (22).
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Data Quality and Integration
Successful implementation of AI-assisted troubleshooting and predictive alerts requires addressing data quality, system integration, and infrastructure challenges. AI-driven predictive maintenance supports Industry 4.0 concepts by improving industrial ecosystem connectivity and interoperability (17). Cloud systems enable scalable, cost-effective implementations, while edge computing ensures real-time, low-latency data processing.
Research emphasizes the importance of data consistency evaluation, network modeling, data standardization, data format transformation, and relational mining to address challenges such as diversity of data sources, data quality issues, inconsistent data formats, and real-time data processing requirements (20). Organizations must also address data security and privacy concerns, which become increasingly critical as systems collect and analyze sensitive production and equipment data (26).
Human-Machine Collaboration
The transition to AI-powered industrial communication requires careful attention to human-machine collaboration. Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-centered approaches that place operators at the system's center, promoting interactive, personalized human-to-machine communication with natural language over graphical and static interactions on traditional human-machine interfaces (4). This approach recognizes that while AI can detect problems, only people can solve them (27).
Successful adoption requires change management frameworks that include clear assignment of roles and responsibilities, updated maintenance procedures and checklists, and continuous feedback loops to track model performance and operational impact (28). Organizations must bridge generational gaps when introducing digital communication to experienced operators accustomed to radio or face-to-face interaction (29).
Future Outlook
The future of industrial communication will be characterized by increasingly sophisticated AI capabilities that seamlessly integrate with human workflows. Continued progress in AI and NLP technologies will lead to systems with enhanced capabilities for understanding, reasoning, and generating human-like responses (30). Deep learning techniques, such as transformer models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), will enable systems to comprehend context more accurately and generate more contextually relevant responses.
Explainable AI (XAI) frameworks will become increasingly important, addressing concerns about model interpretability and building trust in AI-driven decisions (17, 31). These frameworks help organizations understand why AI systems make particular recommendations, enabling better human oversight and continuous improvement.
The integration of AI-assisted troubleshooting, pattern recognition, and intelligent escalation with digital twin technology and Industry 5.0 principles will create truly intelligent manufacturing ecosystems. These systems will not only predict failures and optimize maintenance but also facilitate seamless communication between operators, engineers, and automated systems, creating a more responsive, efficient, and safe industrial environment.
Conclusion
The future of industrial communication lies in the sophisticated integration of AI-assisted troubleshooting, pattern recognition, predictive alerts, and intelligent escalation systems. These technologies are transforming manufacturing from reactive firefighting to proactive, intelligent operations. By leveraging natural language processing, machine learning for anomaly detection, real-time monitoring with digital twins, and smart escalation management, industrial organizations can dramatically reduce downtime, improve safety, and enhance operational efficiency.
As these technologies mature and become more widely adopted, organizations that embrace AI-powered industrial communication will gain significant competitive advantages through reduced costs, improved reliability, and enhanced ability to respond to operational challenges. The journey toward fully intelligent industrial communication has begun, and the opportunities for innovation and improvement continue to expand as AI capabilities advance.
References
-
McKinsey & Company (2015). Predictive maintenance in transportation and logistics. Research report on operational efficiency improvements.
-
Deloitte (2024). The cost of unplanned downtime in industrial manufacturing. Industry analysis report.
-
Master of Code (2025). Understanding NLP chatbots: A comprehensive guide
-
Springer Link (2024). An experimental hybrid customized AI and generative AI chatbot human machine interface to improve a factory troubleshooting downtime in the context of Industry 5.0. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
-
Waylay (2024). GAI: The transformative impact of intelligent bots in troubleshooting
-
Landbot (2025). Natural language processing chatbot: NLP in a nutshell
-
Sinch Engage (2025). NLP: The chatbot technology that will be a gamechanger for your business
-
MathWorks (2024). What is anomaly detection. MATLAB & Simulink documentation.
-
PMC (2023). Machine learning for the detection and diagnosis of anomalies in applications driven by electric motors. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
-
MDPI Electronics (2024). Advanced anomaly detection in manufacturing processes: Leveraging feature value analysis for normalizing anomalous data. Electronics, 13(7), 1384.
-
Wikipedia (2024). Anomaly detection
-
PMC (2023). Anomaly detection in a smart industrial machinery plant using IoT and machine learning. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
-
PMC (2023). A smart-anomaly-detection system for industrial machines based on feature autoencoder and deep learning. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
-
ResearchGate (2024). Artificial intelligence-driven predictive maintenance in manufacturing: Enhancing operational efficiency, minimizing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization
-
AlphaBold (2025). AI predictive maintenance for manufacturing efficiency
-
ScienceDirect (2023). Digital Twin applications toward Industry 4.0: A review
-
SSRN (2024). Patil, D. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Predictive Maintenance In Manufacturing: Enhancing Operational Efficiency, Minimizing Downtime, And Optimizing Resource Utilization
-
MDPI Computers (2024). Digital Twin and 3D Digital Twin: Concepts, applications, and challenges in Industry 4.0. Computers, 13(4), 100.
-
Deloitte Insights (2017). Industry 4.0 and the digital twin technology. Deloitte University Press.
-
Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Digital Twin Systems Engineering Towards the Industrial Metaverse in the Era of Industry 5.0
-
FlowForma (2025). How to automate AI-powered escalation management in 2025
-
Orca Lean (2024). How AI-powered problem-solving tools reduce escalation delays
-
BigPanda (2024). Intelligent alerts and alert management best practices
-
Superwise (2024). Manufacturing AI for predictive maintenance
-
ServiceNEX (2024). Intelligent escalation management
-
IET Information Security (2024). Kumari et al. A comprehensive investigation of anomaly detection methods in deep learning and machine learning: 2019-2023
-
SIGNL4 (2024). Mobile alerting and anywhere incident response
-
Neural Concept (2025). Predictive maintenance machine learning: A practical guide
-
Deloitte (2024). Using AI in predictive maintenance
-
GeeksforGeeks (2025). What is Natural Language Processing (NLP) chatbots?
-
ScienceDirect (2024). An explainable artificial intelligence model for predictive maintenance and spare parts optimization