10 Common Enterprise Ticketing Implementation Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)

According to industry research, 70% of software projects fail, with most failures starting from poor planning and implementation errors.
The good news is that most of these failures are preventable. Here are ten most serious mistakes that derail enterprise ticketing projects... and more importantly, how to avoid them.
1. Skipping the Discovery Phase
The Mistake:
Many organizations rush directly into implementation without proper discovery work. Teams treat discovery as an obstacle rather than necessary preparation, eager to see results quickly. This impatience creates a domino effect of problems that surface months later.
Why It Happens:
Leadership pressure to "go live" quickly, underestimation of project complexity, or false confidence that existing requirements are sufficient. Some teams assume they know what they need without validating those assumptions.
The Impact:
More than half of failed software projects go wrong due to overlooked requirements in the early development phases. Without thorough discovery, organizations face mid-project scope changes, budget overruns of 200-300%, and systems that don't meet actual user needs.
How to Avoid It:
-
Allocate 2-8 weeks for discovery depending on project complexity. This isn't wasted time—projects with proper planning phases are 40% more likely to finish on time
-
Conduct stakeholder interviews across all departments that will use the system
-
Document current workflows and pain points before designing new ones
-
Validate assumptions with real users through surveys and focus groups
-
Create a detailed requirements document that everyone signs off on
Pro tip: Discovery typically saves 3-5x its cost in avoided development waste.
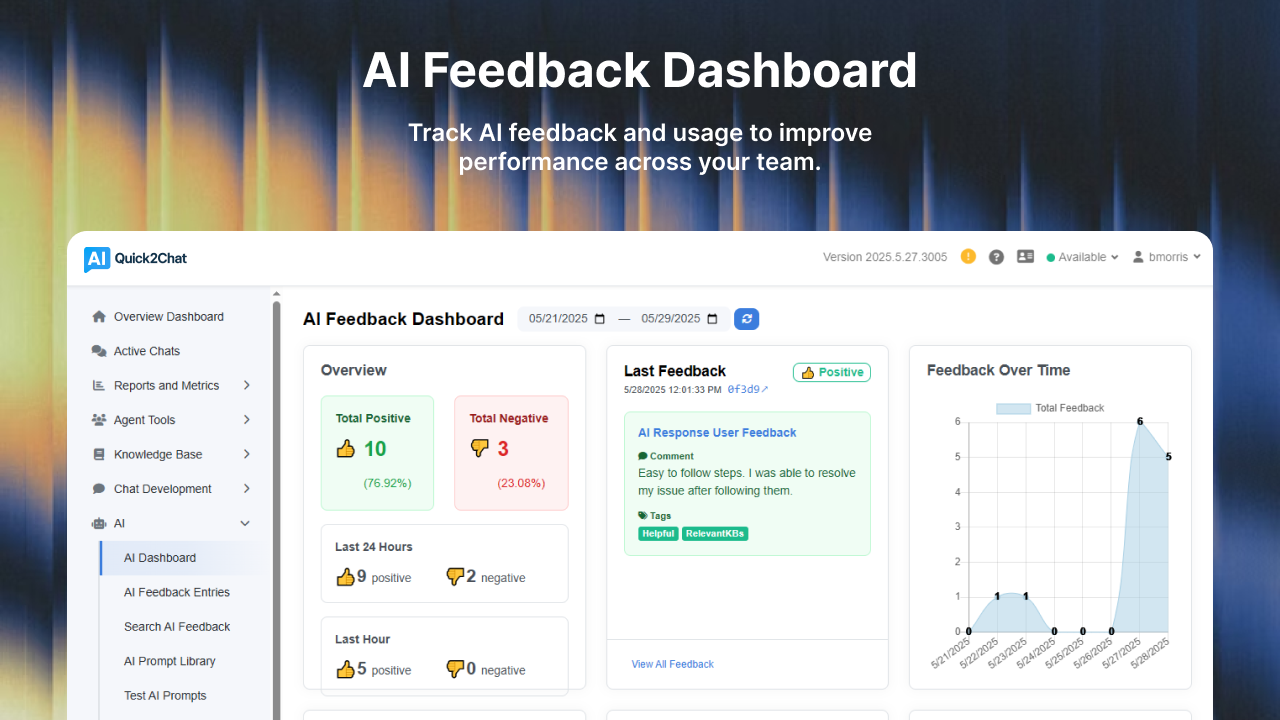
2. Failing to Establish Clear Goals and KPIs
The Mistake:
Many organizations rush into implementing customer support software without first establishing clear goals. They know they need "better ticketing" but haven't defined what success looks like.
Why It Happens:
Teams focus on features rather than outcomes. They get excited about automation capabilities without asking: "What specific problem does this solve?"
The Impact:
Without clear objectives, you can't measure ROI, justify the investment, or course-correct when needed. Teams argue about whether the implementation is succeeding because there's no shared definition of success.
How to Avoid It:
-
Define specific, measurable KPIs before selection, such as:
-
Reduce first response time from 24 hours to 10 hours
-
Improve customer satisfaction scores by 25%
-
Decrease ticket resolution time by 30%
-
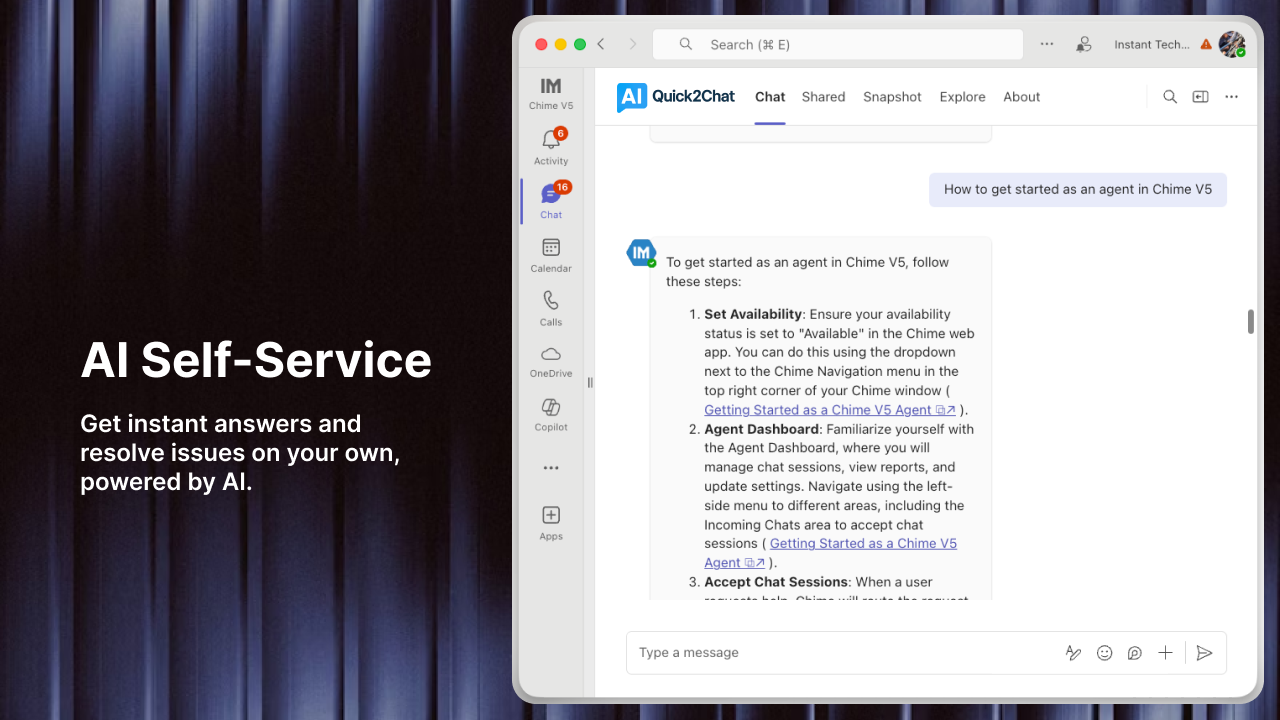
Achieve 70-80% self-service adoption
-
-
Gather input from all stakeholders on what success means to them
-
Document baseline metrics from your current system
-
Set realistic timelines for achieving each goal
-
Review progress quarterly and adjust strategies as needed
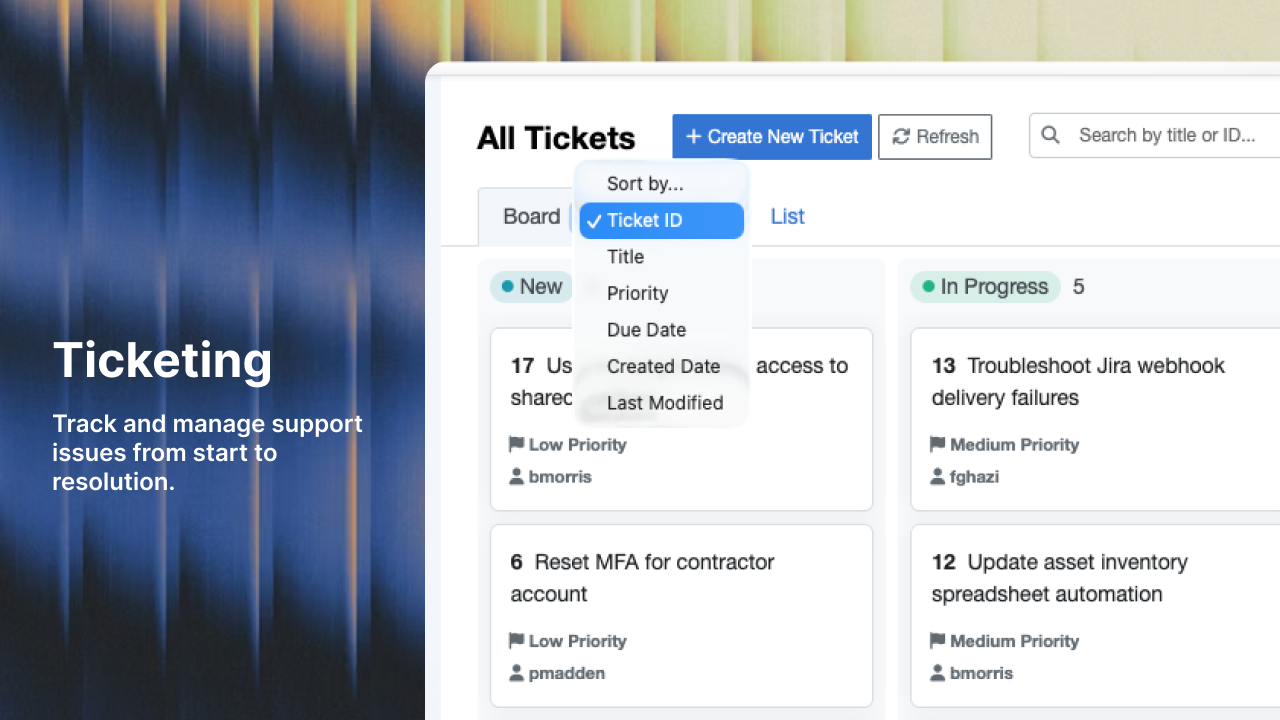
3. Choosing the Wrong System for Your Needs
The Mistake:
Failing to select the right ticketing solution for your IT help desk may result in a complex implementation and reduced ROI. Organizations either over-buy enterprise features they'll never use, or under-buy and outgrow the system within a year.
Why It Happens:
Impressive demos, aggressive sales tactics, or choosing based on price rather than fit. Teams fail to perform systematic audits to determine their IT maturity, size and scale of operations.
The Impact:
Wasted budget on unnecessary features, insufficient functionality requiring workarounds, or need for a costly re-implementation within 18-24 months.
How to Avoid It:
-
Conduct an honest assessment of your organization's maturity and needs
-
Consider your 3-year growth trajectory, not just current needs
-
Evaluate scalability: Can the system grow with you?
-
Test integration capabilities with existing tools (CRM, monitoring, CMDB)
-
Look beyond features to vendor support, community, and upgrade paths
-
Request references from similar-sized organizations in your industry
-
Run a pilot program with 2-3 finalist solutions before final selection
4. Poor Change Management
The Mistake:
Failure to consider the human element is one of the most common implementation pitfalls. Technical teams focus on configuration and data migration while ignoring the people who will use the system daily.
Why It Happens:
Change management feels "soft" compared to technical implementation. IT teams assume that if the system works technically, adoption will follow naturally.
The Impact:
User resistance, low adoption rates, shadow IT workarounds, and possible abandonment of the new system. Resistance to change can derail even technically perfect implementations.
How to Avoid It:
-
Involve stakeholders early in the planning process. People affected by the implementation need to know that the new system will improve their work lives
-
Build a shared vision by communicating benefits clearly and honestly
-
Create a change management plan addressing:
-
Communication strategy
-
Training approach
-
Support resources
-
Feedback mechanisms
-
-
Identify champions in each department to advocate for the system
-
Address concerns transparently, including limitations
-
Celebrate early wins to build momentum
-
Provide ongoing support beyond the initial launch
Timely, accurate and honest communication builds trust between key stakeholders.
5. Insufficient Training and Support
The Mistake:
Organizations provide one-time training sessions during implementation, then expect users to remember everything. Poor training affects efficiency and leads to choosing the wrong ticketing system features.
Why It Happens:
Budget constraints, timeline pressure, or assumption that the system is "intuitive enough" not to need extensive training.
The Impact:
Frustrated users, inefficient workflows, ticket backlogs, poor data quality, and calls for returning to the old system.
How to Avoid It:
-
Provide thorough training across multiple formats:
-
Live sessions for core workflows
-
Recorded videos for reference
-
Written documentation and job aids
-
Hands-on practice environments
-
-
Create role-specific training rather than one-size-fits-all
-
Identify and train "super users" who can provide ongoing support
-
Establish a knowledge base with FAQs and troubleshooting guides
-
Offer refresher sessions 30, 60, and 90 days post-launch
-
Maintain office hours where users can get help with specific issues
-
Gather feedback on training effectiveness and adjust as needed
Remember: Training materials and an online knowledge base should be available to support their learning.
6. Poor Data Migration Planning
The Mistake:
Teams fail to cleanse and organize data before migration, leading to inconsistencies. Historical tickets, customer information, and knowledge articles are migrated "as-is" without cleanup.
Why It Happens:
Migration is viewed as a technical task rather than a data quality opportunity. Teams underestimate the time required for proper data preparation.
The Impact:
Garbage in, garbage out. Poor data quality in the new system leads to incorrect reporting, duplicate records, and user frustration.
How to Avoid It:
-
Audit existing data 2-3 months before migration
-
Identify what needs to be migrated vs. archived
-
Clean data systematically:
-
Remove duplicates
-
Standardize formats
-
Validate important fields
-
Update outdated information
-
-
Map old fields to new system carefully
-
Run test migrations and validate results
-
Execute migration in phases if possible (pilot group first)
-
Verify data integrity after migration with spot checks
-
Have a rollback plan in case of serious issues
7. Over-Customization and Configuration Complexity
The Mistake:
Too much customization can harm usability. Teams configure every possible option, create dozens of custom fields, and build elaborate workflows that become impossible to maintain.
Why It Happens:
Desire to replicate exact current processes, or trying to accommodate every stakeholder's "nice-to-have" request without prioritization.
The Impact:
System becomes slow, confusing, and difficult to upgrade. Admin overhead skyrockets. User adoption suffers because the system is too complex.
How to Avoid It:
-
Start with out-of-the-box functionality and customize only where necessary
-
Challenge existing processes: "Should we do it this way?" not "Can we do it this way?"
-
Prioritize customizations using MoSCoW method (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won't have)
-
Consider long-term maintenance costs of each customization
-
Document all customizations and their business justification
-
Review quarterly and remove unused customizations
-
Use standard features even if they require process changes
8. Ignoring Integration Requirements
The Mistake:
Teams implement ticketing systems as standalone solutions without properly integrating with other business tools. Important data lives in silos across multiple systems.
Why It Happens:
Not making sure the AI solution can integrate systems beyond immediate needs. Integration is treated as a "phase 2" item that never happens.
The Impact:
Agents must switch between multiple systems to resolve tickets, leading to longer resolution times, data inconsistencies, and poor customer experience. Manual data entry creates errors and wasted time.
How to Avoid It:
-
Map integration requirements during discovery phase
-
Prioritize necessary integrations for launch day:
-
Identity management (SSO/LDAP)
-
Email systems
-
CRM or customer database
-
Monitoring and alerting tools
-
CMDB or asset management
-
-
Evaluate API capabilities and documentation quality
-
Plan for bi-directional data flow where needed
-
Test integrations thoroughly in pre-production environment
-
Monitor integration health post-launch with alerts for failures
-
Document integration dependencies for troubleshooting
9. Launching Without Sufficient Testing
The Mistake:
Organizations rush to production without thorough testing, or test only "happy path" scenarios. Edge cases, high-volume situations, and error handling get overlooked.
Why It Happens:
Timeline pressure, stakeholder impatience, or overconfidence that vendor testing is sufficient.
The Impact:
Production issues that destroy user confidence, emergency fixes during business hours, and damage to the project's reputation.
How to Avoid It:
-
Create thorough test plans covering:
-
Functional testing (does it work as designed?)
-
Integration testing (do systems communicate correctly?)
-
Performance testing (can it handle expected volume?)
-
User acceptance testing (do users find it usable?)
-
Security testing (are vulnerabilities addressed?)
-
-
Include negative testing: What happens when things go wrong?
-
Test with real users performing actual tasks
-
Simulate high-volume scenarios to identify bottlenecks
-
Document test results and track issues to resolution
-
Conduct a pilot rollout with a small group before full deployment
-
Have a rollback plan and test it
10. Neglecting Post-Implementation Optimization
The Mistake:
Teams treat "go-live" as the finish line. Implementation timelines vary but typically range from a few weeks for basic systems to several months for complex, enterprise-level solutions—but the work doesn't stop there.
Why It Happens:
Project fatigue, team reassignment to other priorities, or lack of continuous improvement culture.
The Impact:
System stagnation, declining user satisfaction, missed opportunities for optimization, and failure to achieve projected ROI.
How to Avoid It:
-
Schedule regular reviews (30, 60, 90 days, then quarterly):
-
Review KPIs against baseline
-
Analyze ticket patterns and trends
-
Identify bottlenecks and pain points
-
Gather user feedback systematically
-
-
Establish a continuous improvement process:
-
Regular governance meetings
-
Feedback collection mechanisms
-
Prioritization framework for upgrades
-
Testing protocols for changes
-
-
Monitor system performance and address issues proactively
-
Update knowledge base based on common tickets
-
Refine automations as you learn usage patterns
-
Provide ongoing training for new features and best practices
-
Celebrate successes and share metrics demonstrating value
The Cost of Mistakes vs. The Value of Getting It Right
The financial effect of these mistakes is staggering. Budget estimates typically achieve within 15% accuracy with thorough discovery, compared to 200-300% overruns in projects that skip this phase.
Consider this example: A mid-sized company implementing an enterprise ticketing system discovered through proper discovery that they needed better integration with their monitoring tools. This finding, which took two weeks to find, prevented what would have been a six-month post-launch integration project costing $200,000.
On the flip side, success stories abound. Organizations using proper implementation methodologies have seen 3x improvements in first response time and 30% of knowledge base articles approved for ticket deflection.
Your Implementation Success Checklist
Before you begin your enterprise ticketing implementation, make sure you can answer "yes" to these questions:
Discovery & Planning
-
Have we completed a thorough discovery phase?
-
Are our goals and KPIs clearly defined and agreed upon?
-
Have we documented current state and desired future state?
-
Do we have executive sponsorship and adequate budget?
System Selection
-
Have we evaluated multiple solutions against our requirements?
-
Have we validated scalability and integration capabilities?
-
Have we spoken with reference customers?
-
Have we conducted a pilot or proof of concept?
People & Change
-
Have we created a change management plan?
-
Have we identified stakeholders and champions in each department?
-
Have we communicated the "why" behind this change?
-
Are we prepared to address resistance constructively?
Training & Support
-
Have we developed role-specific training materials?
-
Have we identified and trained super users?
-
Have we created accessible documentation and knowledge base?
-
Do we have a support plan for the first 90 days?
Technical Implementation
-
Have we cleaned and prepared data for migration?
-
Have we prioritized and limited customizations?
-
Have we tested all critical integrations?
-
Have we conducted comprehensive testing including edge cases?
Post-Launch
-
Do we have a monitoring plan for system health and performance?
-
Have we scheduled regular review meetings?
-
Do we have a process for collecting and acting on user feedback?
-
Have we planned for continuous optimization?
Final Thoughts
Enterprise ticketing implementation doesn't have to be a high-risk project. While the statistics about project failures are sobering, they represent organizations that fell into predictable traps.
Avoiding these ten common mistakes dramatically increases your chances of delivering a system that users embrace, stakeholders value, and that delivers measurable ROI. The secret is recognizing that successful implementation is as much about people, processes, and planning as it is about technology.
Any successful implementation begins with excellent communication, which in turn forms a bond of trust. Start there, follow these guidelines, and you'll position your organization for ticketing excellence.